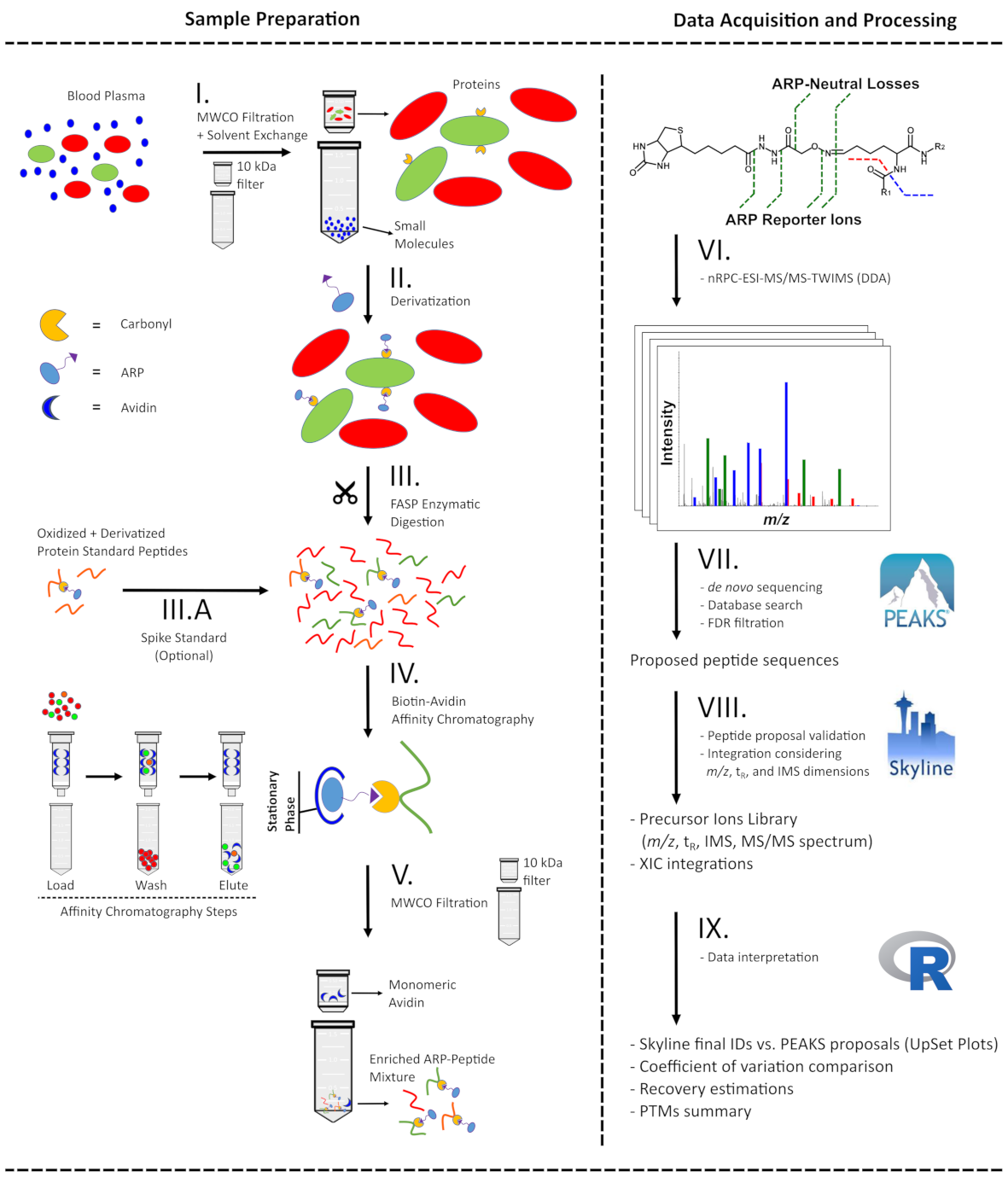
Schematic presentation of the analytical workflow applied to plasma samples for ARP-peptide enrichment (left) and the following LC-MS-based analysis from acquisition to data processing (right). Ultrafiltration of blood plasma was applied to simultaneously remove small molecules and reconstitute proteins in acidic conditions (I) to derivatize carbonylated proteins with ARP (II). Proteins were digested with trypsin using a FASP approach (III) and the resulting peptide mixture was split and either mixed with an ARP-labelled digest of a model protein (III.A) or directly enriched by avidin-affinity chromatography (IV). The fractions were submitted to ultrafiltration to remove interfering monomeric avidin (V) and analyzed by nRPC‑ESI‑MS/MS-TWIMS in DDA mode (VI). The generated tandem mass spectra were processed with a hybrid de novo and database search approach (VII) considering specific ARP fragmentation patterns. All proposed ARP-peptides were validated by manual annotation of the mass spectra and considering both drift times in IMS and retention times in RPC (VIII). The filtered peptide list and corresponding peak areas were further processed (IX) to assess recovery, sample preparation workflow reproducibility, and protein carbonyl modification site location.